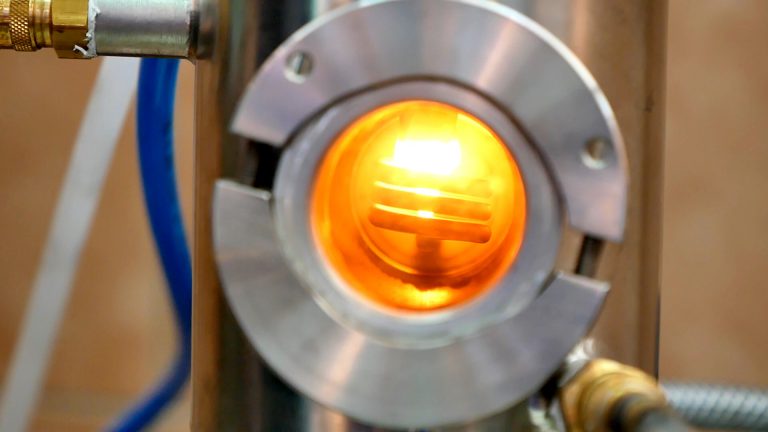
Melting of reactive metals
Melting of metals without the use of protective atmospheres or vacuum techniques, in some cases prevents the proper conduct of the process due to the reactions of the heated metal with oxygen and other gases contained in the air. An example can be the problem with melting of titanium, which by binding with oxygen changes its structure practically at once.
Melting in a protective gas atmosphere, such as argon, is often insufficient.
Stands consisting of an induction furnace, the inductor of which is located in a vacuum chamber, and a set of pumps, including high vacuum pumps, allow for complete elimination of impurities that could change the composition of the metals being melted.
@EnergoEl - All rights reserved.
We use cookies on our website to provide you with the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking "Accept", you agree to the use of ALL cookies.
Manage consent
Privacy Overview
This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Functional cookies help to perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collect feedbacks, and other third-party features.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. These cookies track visitors across websites and collect information to provide customized ads.
Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet.
- About Us
- Products
- Technologies
- Hardening
- Soldering
- Carbide brazing
- Brazing of CO radiators
- Brazing of electrotechnical components
- Hard soldering of silver contacts
- Brazing of inductors
- Brazing of water and gas connections
- Soldering of titanium
- Soft soldering of electronic components
- Soft soldering of high frequency connectors.
- De-soldering of components for metal recovery
- Melting of metals
- Forging and forming
- Other technologies
- Continuous drying of paints and coatings
- Softening of ultrasonic seams
- Vacuum spraying
- Heating of anodized parts before bending
- Heating pipes before bending
- Pre-weld heating
- Preheating of wire ropes
- Connections based on temperature expansion
- Fusing inserts into plastics
- Induction welding
- Induction welding of seamed tubes
- Diffusion welding
- Thermal dimension calibration
- Letting go / relaxing
- Melting reactive metals
- Powder sintering
- Services
- Gallery
- Contact